



Next: Choices for Preconditioner
Up: NSPCG User's Guide
Previous: Introduction
Usage
The calling sequence for the package is
CALL NSPCG (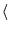 precon
precon 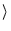 ,
,
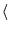 accel
accel 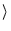 ,NDIM,MDIM,N,MAXNZ,COEF,JCOEF,P,IP,U,UBAR,RHS,
,NDIM,MDIM,N,MAXNZ,COEF,JCOEF,P,IP,U,UBAR,RHS,
WKSP,IWKSP,NW,INW,IPARM,RPARM,IER)
where
 precon
precon 
- is the name of a preconditioning routine which must
be declared EXTERNAL in the user's calling routine. It
must be one of a certain number of choices given in
Section 3. [name]
 accel
accel 
- is the name of an acceleration routine which must
be declared EXTERNAL in the user's calling routine. It
must be one of a certain number of choices given in
Section 4. [name]
- NDIM
- is the row dimension of the COEF array (See
Section 8 on Storage Modes for more information).
[integer, input]
- MDIM
- is the column dimension of the COEF array (See
Section 8 on Storage Modes for more information).
[integer, input]
- N
- is the order of the linear system. [integer, input]
- MAXNZ
- is the active column width of the COEF array (See
Section 8 on Storage Modes for more information).
[integer, input/output]
- COEF
- is a real array containing the matrix nonzero coefficients
in one of several possible formats to be given in
Section 8. [real, input/output]
- JCOEF
- is an integer array containing auxiliary matrix nonzero
information corresponding to COEF. [integer, input/output]
- P
- is an integer vector. If no permutation is to be applied
to the matrix, then P is unused and may be dimensioned
to be of length one.
If the matrix is to be permuted into another
form, such as red-black, P is a coloring vector of length N
indicating the integer coloring number of each equation.
On output, P is then the permutation vector corresponding
to the multi-color ordering. (See Sections 11 and
12 for more details.) [integer, input/output]
- IP
- is an integer vector. If no permutation is to be applied
to the matrix, then IP is unused and may be dimensioned
to be of length one.
If the matrix is to be permuted, IP is an integer workspace
vector of length N on input and the inverse permutation
vector corresponding to P on output. (See Sections 11
and 12 for more details.) [integer, output]
- U
- is a real vector of length N containing the current
estimate of the solution to the linear system on
input. The user must supply an initial guess, which
can be all zeros if no information is known. On
output, U contains the solution estimate computed by
the package. [real, input/output]
- UBAR
- is a real vector of length N containing the exact solution
to the linear system, if known. This vector is used
only if the exact stopping test is used. Otherwise,
it may be dimensioned to be of length one. (See
Section 10 for information on the available
stopping tests.) [real, input]
- RHS
- is a real vector of length N containing the right-hand-side
of the matrix problem. [real, input]
- WKSP
- is a real vector of length NW used for workspace.
[real, input]
- IWKSP
- is an integer vector of length INW used for workspace.
[integer, input]
- NW
- is an integer variable indicating the length of the
WKSP vector on input and the amount used on output.
If insufficient real workspace is provided, NW is
set on output to the amount of workspace needed
at the point execution terminated. (See Section 9
for suggested initial values.) [integer, input/output]
- INW
- is an integer variable indicating the length of the
IWKSP vector on input and the amount used on output.
If insufficient integer workspace is provided, INW is
set on output to the amount of workspace needed
at the point execution terminated. (See Section 9
for suggested initial values.) [integer, input/output]
- IPARM
- is an integer vector of length 25 giving various
integer parameters which are described in Section
7. [integer, input/output]
- RPARM
- is a real vector of length 16 giving various real
parameters which are described in Section 7.
[real, input/output]
- IER
- is an error flag. A nonzero value on output indicates
a fatal or warning error was detected during the
iteration. (See Section 13 for a list of error
codes.) [integer, output]




Next: Choices for Preconditioner
Up: NSPCG User's Guide
Previous: Introduction
![]() precon
precon ![]() ,
,
![]() accel
accel ![]() ,NDIM,MDIM,N,MAXNZ,COEF,JCOEF,P,IP,U,UBAR,RHS,
,NDIM,MDIM,N,MAXNZ,COEF,JCOEF,P,IP,U,UBAR,RHS, ![]() precon
precon ![]()
![]() accel
accel ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()